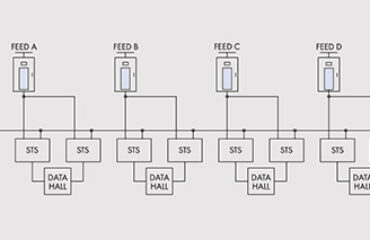
The way we use UPS systems today has changed a lot. Technological improvements in UPS efficiency, versatility and flexibility have enabled Borri to approach nonstandard UPS applications such as peaking shaving and power buffering. These techniques are in turn related to UPS systems being able to fulfill the demand of integration into Smart Grids.
In this article we get a closer look at how peak shaving works and why smart grids are a high-potential application field for UPS manufacturers. To do so, we’ve answered some of the most common questions when talking about peak shaving UPS and their integration with smart grids.
-
What is peak shaving?
Peak shaving is a set of techniques aiming to keep the electrical energy demand curve as flat as possible throughout the day and the year, by canceling peaks. Energy consumers with peak shaving capability, will interact with the supplying mains, in order to decrease their power absorption during high energy demand periods. These include peak factory workload or massive use of air conditioning systems on hot summer days, among others.
-
What is a smart grid?
In conventional grid arrangement, power is generated by big scale facilities and then conveyed to consumers in a one direction energy flow. In a smart grid, power generation is distributed among both big power plants and smaller production sites, mostly coming from renewable energy sources. To the widest extent, residential PV generators can be part of a smart grid. Embedded ICT provide the required information capability for grid stability control.
-
Why energy storage is so important in smart grids?
One purpose of a smart grid is to exploit as much renewable energy as possible, which is highly variable and requires local energy storage to buffer the produced energy for constant use. One of the preferred energy storage types is Li-Ion chemistry, as Li- Ion batteries are highly suitable for partial discharge or cyclic use. Their low weights and relatively wide temperature range also makes them ideal for setting up large energy storage provisions, as well as distributed energy sources.
-
Why is peak shaving needed?
Energy production and distribution infrastructure must be sized according to peak demand. If peak demand is much higher than the average, grids will need to be oversized, thus the return on investment for the providers will be longer.
Furthermore, sudden variations in load demand can result in grid frequency and voltage instability, leading to mains quality deterioration and in turn further costs for the provider. Grid operators are therefore keen on finding ways to achieve a “shaved curve”; on the other hand, users who are available to implement a peak shaving program, will usually be granted a rebate on their energy bills.
-
How does UPS peak shaving work?
The easiest way for a UPS to decrease grid power absorption is to idle the AC/DC rectifier stage and switch to battery power. Stored energy will therefore supply loads through the UPS DC link for the required duration. To properly operate, battery power is to be sized for the required backup time upon mains failure plus the required peak shaving time. This technique is also known as “Passive Grid Tie”. More complex implementation uses bidirectional rectifiers, so that the UPS can reject energy onto the grid in “Active Grid Tie” schemes.
Active ties are more flexible when it comes to delivering different amounts of energy in time, on the other hand they require further hardware and control logic, besides being subjected to local grid tie regulations. Control logic for peak shaving span from simple on/off, with an external dispatcher unit enabling the feature, to sophisticated UPS algorithm, monitoring the upstream grid’s quality and commanding the system accordingly to adapt power absorption.
-
What’s on the horizon for UPS systems in the coming years?
UPS will be more and more embedded in electricity grids, and they are going to play an important role in the Internet of Things world. As smart grids spread across the world, so will uninterruptible services, requiring UPS to backup large facilities as well as residential buildings. Energy is a predominant component in the circular economy and UPS manufacturers are being asked to reduce their environmental footprint, by focusing their development on reducing energy and CO2 exploitation during their whole lifecycle, and setting up second-life and recycling strategies.
This emerging market is offering interesting opportunities in many verticals such as data centers, industry and healthcare. Borri has recently developed and deployed UPS solutions in the range of 60-400 kVA with power buffering capability, supplying medical equipment.
By limiting the input power to the regime value, the UPS units ensures that the frequent energy peaks absorbed by MRI equipment or CT scanners are not drawn by the public utility. End users can therefore downsize their energy requirement and their upstream equipment accordingly, thus achieving permanent substantial savings in their energy bills.
If you want to know more about our peak shaving UPS’s and smart grid solutions, please dropo us an email at info@borri.it


 Global
Global  Italiano
Italiano  Deutsch
Deutsch